‘Statistically, that shouldn’t have happened’: Something very weird occurred in the ocean after the dinosaur-killing asteroid hit

About 66 million years ago – maybe Sreamer Unlucky Day in May – He smashed an asteroid on our planet.
Fallout was immediately and violent. Evidence 70% of the species is extinct It is not only the famous dinosaurs who once followed the land. The masters of the Mesozoic oceans were also destroyed. MOSAASURLAR – A group of water in water on the top of the food chain – known as the elegant shelled calamari relatives ammonics.
Even groups that wear disasters such as mammals, fish and flowering plants, serious population decreases and species loss. The invertebrate life in the oceans did not give much better results.
But to foam on the sea base, He left a fantastic fossil record And today it continues to develop: double crustaceans – Oyster, rooster, mussel, oyster and more.
It tells an important story about both the past and the future of biological diversity, both the past and the future of biological diversity.
Surprising discoveries on the sea base
Seaside Three quarters of their species were lost This mass, which points to the end of the Cretaceous period, during extinction. My colleagues And me – Each of us who examined biodiversity – Paleobiologist – hoped that the loss of so many species will seriously reduce the various roles played by couples in their circles and the various roles we call “life modes”.
But we Explain in a study This was not the case in Sciences Advances. While evaluating the fossils of thousands of double bubbles, we found that at least one species of almost all lifestyles, regardless of how rare or specialized.
Statistically, this should not be. Randomly kill 70% of Bivalve species and some lifestyles should be lost.
Relating to: The 5 mass extinction events that shape the history of the world – and 6.
Most of them enter the sand and mud in a double -shelled manner and feed on phytoplankton. But others adopted chemosimbionts And Fotosymbonts – Bacteria and algae that produce nutrients for farms from chemicals or sunlight in exchange for housing. There are a few even be a carnage. Some groups including oyster A difficult cement Hardens under water and holds the mussel rocks Silkish yarns rotating.
Certainly, we thought that more specialized lifestyles will be influenced by the effects of the asteroid effect, including photosynthetic algae and bacteria, which prevents the sunlight of dust and debris and disrupts a large part of the food chain of farms. Instead, although biological diversity was mixed forever as a new ecological landscape emerged, most of them insisted. As the dominant species fought, evolutionary newcomers rose to their places.
The reasons why some species survive and others do not leave many questions to explore. Those who filter the phytoplachton from the water column were exposed to some of the highest species losses, but so are the species fed with organic scrap and do not trust solar energy too much. Dight geographical distributions and different metabolisms may have contributed to these extinction models.
Biodiversity Returns
Life is back from each of them Big Five Five Mass Throughout the history of the world, the past diversity is finally piercing. Rich fossil recording and The magnificent ecological diversity of Bivalves It offers a great opportunity to examine these rebounds to understand how ecosystems and global biological diversity were rebuilt after extinction.
The extinction caused by the asteroid strike overturned some developing lifestyles and opened the door to dominate the new view of others.
Many people burned the loss of dinosaurs, malachologists Rudists.
These strange -shaped double crustaceans looked like giant ice cream concentrates, sometimes reached more size than 3 feet (1 meter), and similar to today’s coral reefs, they dominated the shallow, tropical mesozoic seas as large aggregations of twisted individuals. At least a few Moving fotosymbiiotic algaeHe encouraged them to grow like modern corals that provide them with nutrients.
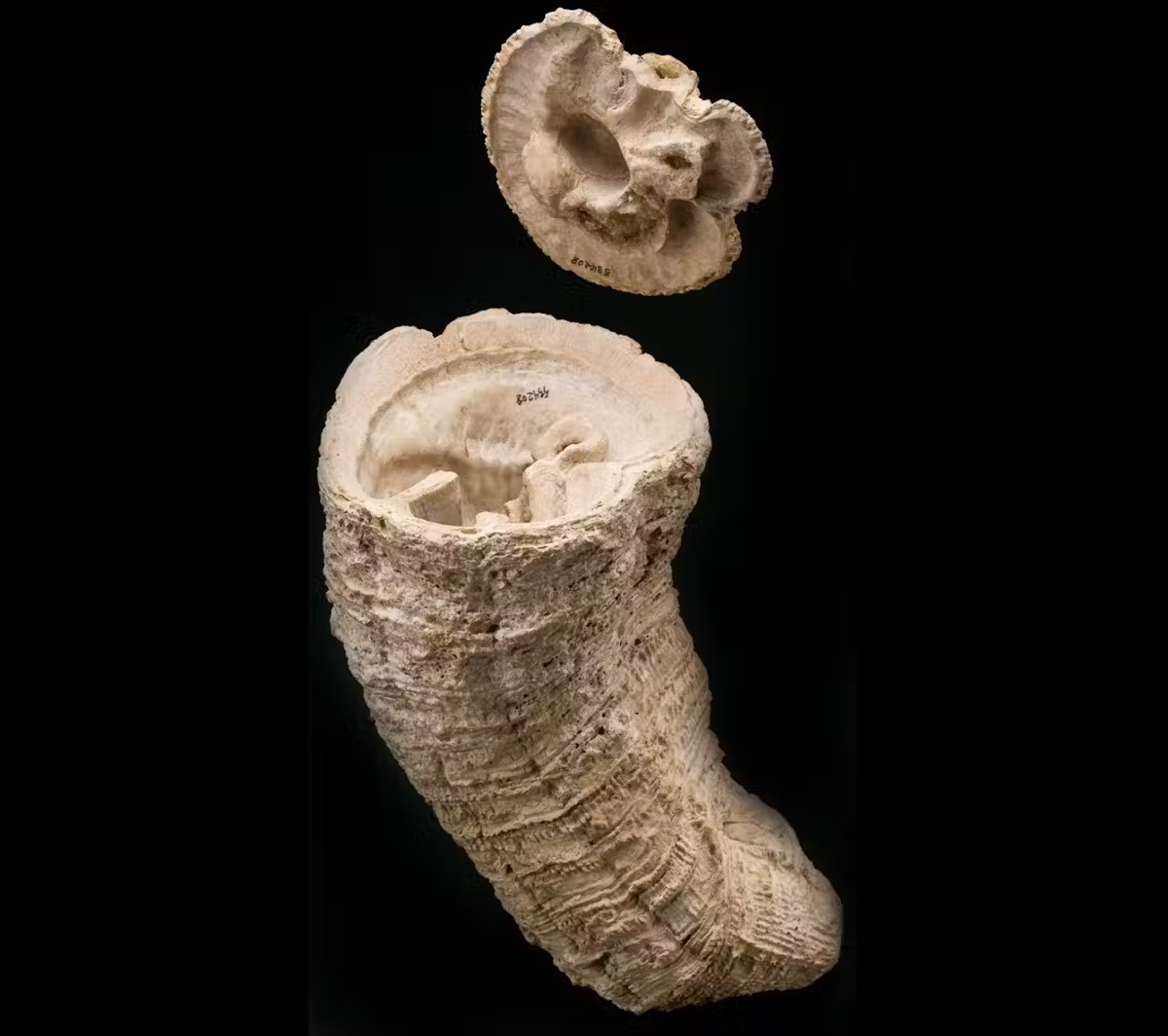
Today giant oyster (Tridacna) and relatives Fill the parts of these unique photosymbiotic lifestyles, which were once occupied by Rudists, but they lack the amazing genre of the Rudists.
Mass extinction clearly increases the status quo. Now, on our ocean floors, sand and mud, quahogs, cockles and relatives are buried – a very different scene from the sea base 66 million years ago.
New winners in a whipped ecosystem
Ecological features alone did not fully predict the patterns of extinction, nor do they completely explain the rebound. In addition, we see that getting rid of a mass extinction does not have to provide a leg as diversified species in old and sometimes new lifestyles – and a few of these new modes dominate the ecological landscape today.
Like Rudists, There were many different types of trigoniid farms Before the extinction. This extremely fancy oyster pearl – Imagine the volcano pearls – and there were hinges passing the fracalizal that holds the two valves together.
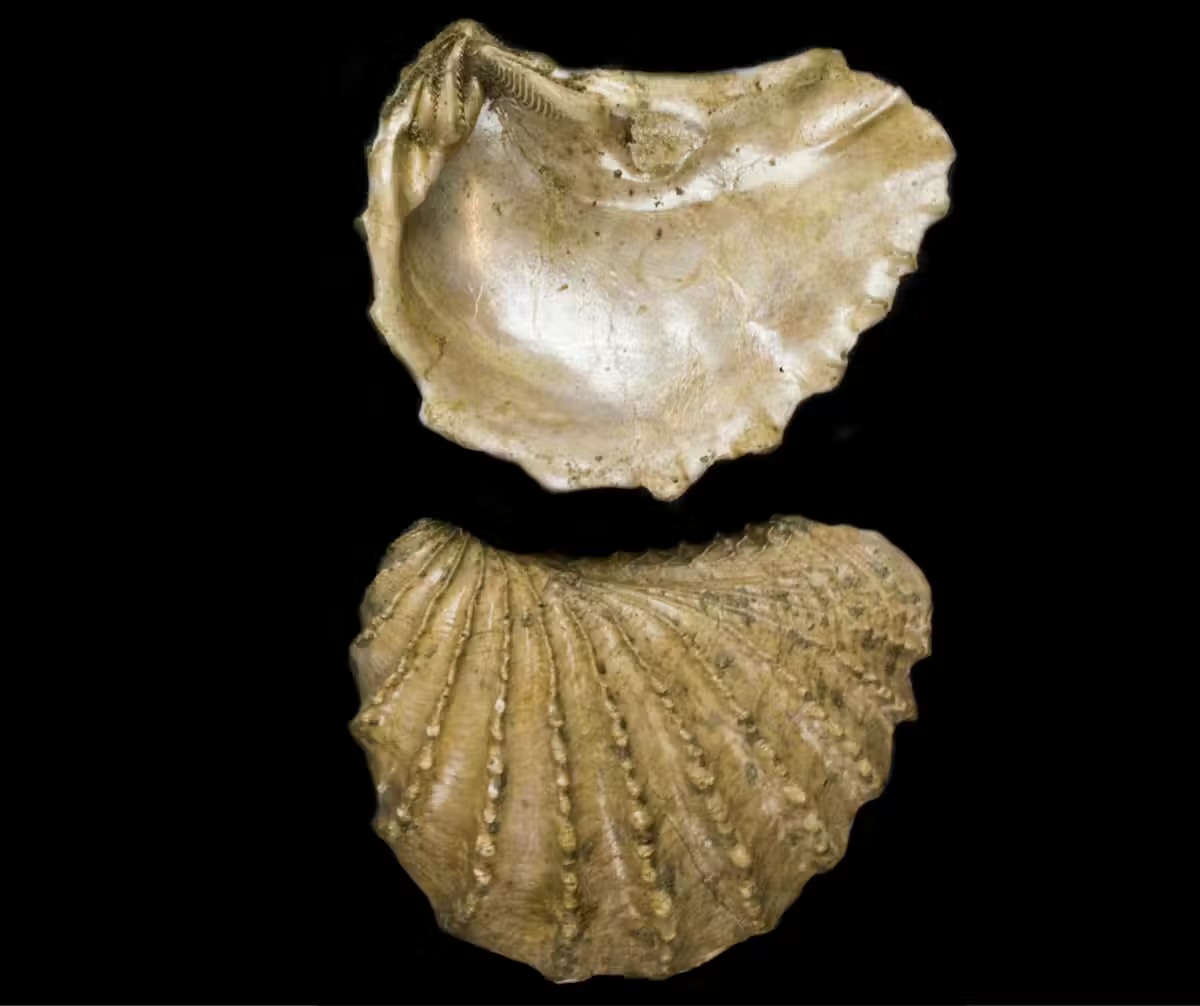

However, although he survived without disappearing without disappearance, he should place the species in the primary position The diversification jumped. Instead, other types of farm, which transforms its living in the same way, once left a strong and global group now only a handful of the Australian coast.
Lessons for today’s oceans
This unexpected extinction and survival patterns can give lessons for the future.
Fossil recording indicates that biological diversity usually has certain breaking points during a perfect storm. climate and environmental turmoil. Not only the loss of species, but the ecological landscape was overturned.
Many scientists, the current biological diversity crisis Sixth Mass DestructionThis is directed by changing ecosystems and human activities with global climate. Mercanlar, who is the host with reefs Almost quarter Known sea species encounter Collective bleaching events In heating, ocean water risks their future. Oceans may also be acidification while absorbing more carbon dioxide Weaken the shells Very important organisms for ocean food network.
Findings like ours show that the recovery obtained from extinction in the future will probably cause many different kinds of mixtures and lifestyles in the oceans. And the result It may not be suitable for human needs If the species that provide a large part of the ecosystem services are genetically or functionally extinct.
Global oceans and inhabitants are complex, and as the latest research of our team, it is difficult to predict the orbit of biological diversity back – even if the oppression of extinction decreases.
Billions of people Linked to the ocean for dinner. Like History Saved According to the world’s bivalves shows, the rise of the turmoil – the number of species in all mode of life – the next time will not settle in an arrangement that can feed many people.
This article, Speech Creative under license. Read original article.




